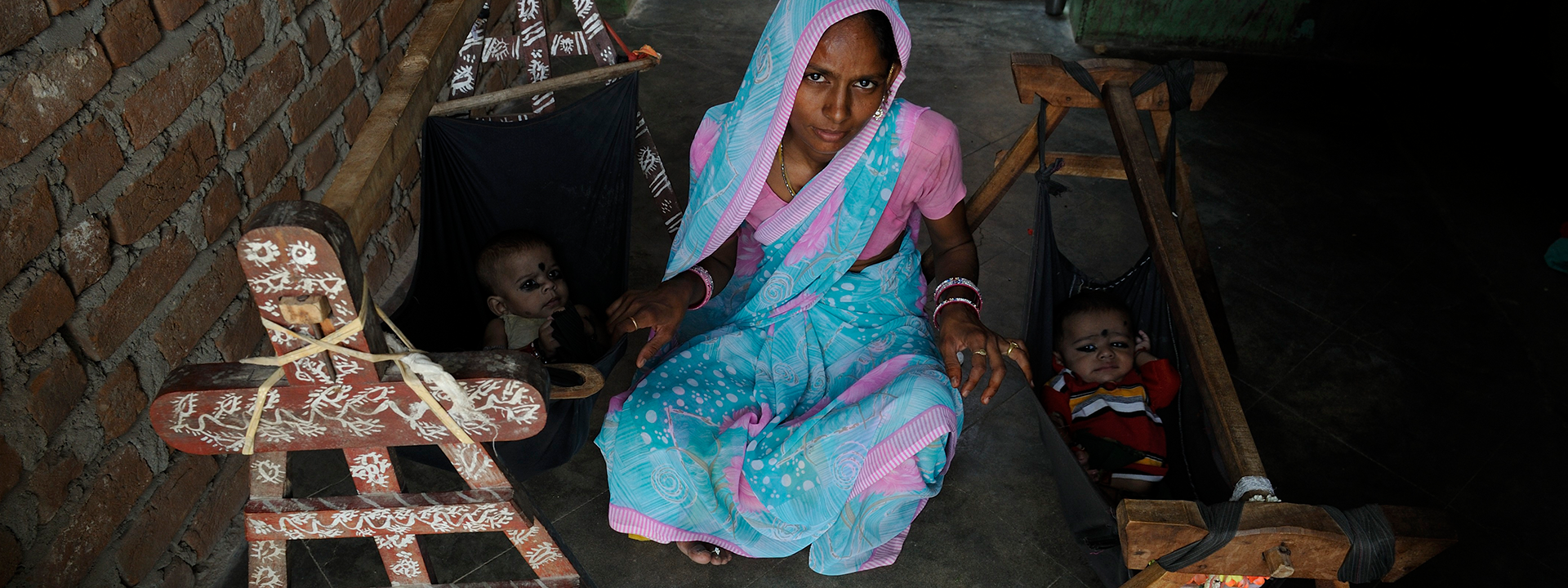


decline in Maternal Mortality Ratio from 212 (2007-09)1 to 97 (2018-20)2
pregnant women died from avoidable causes in 2020, accounting for 8% of global maternal deaths3

decline in Neonatal Mortality Rate from 41 (2011)5 to 31 (2020)6
children under the age of 5 died from avoidable and treatable causes in 2020, accounting to 16% of global Under 5 deaths7

children under the age of 5 die from pneumonia, the second highest burden globally8

children under the age of 5 die from Diarrhea, the highest burden globally8

Nearly
women delivered in a health facility9
An improvement from 79% (2015-16) to 89% (2019-21)9
pregnant women did not receive the recommended four ANC checkups9
Proportion of mothers receiving at least four ANCs improved from 51% (2015-16)
to 58% (2019-21)9

women did not receive the recommended postnatal visit within 2 days of delivery9

By 2030, India aims to reach a Maternal Mortality Ratio of 70.
By 2030, end preventable deaths of newborns and children under 5 years of age, aiming to
reduce neonatal mortality to at least as low as 12 per 1,000 live births and under-5 mortality to at
least as low as 25 per 1,000 live births.
IHAT and The University of Manitoba are working in close collaboration with the Government of Uttar Pradesh to improve availability, quality and utilisation across the community, facility and systemic level for maternal, newborn and child health outcomes.
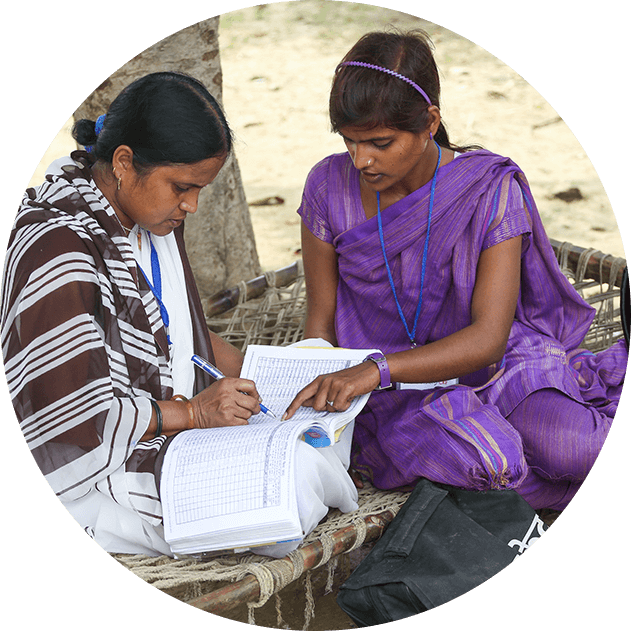
IHAT works with the government to enhance the coverage and quality of antenatal care, birth planning, home-based maternal, newborn, child health services and immunisation.
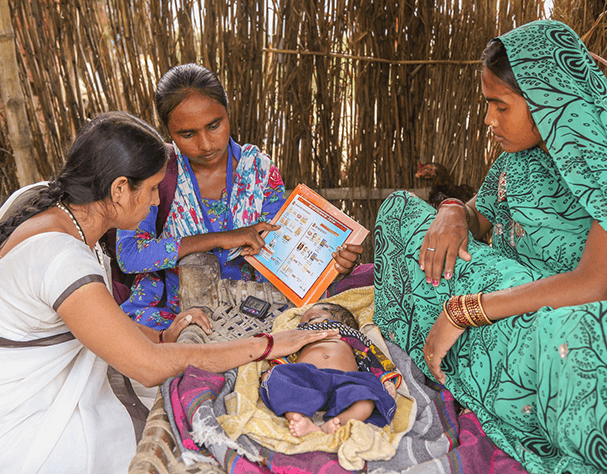
We build the capacity of Frontline Workers to mobilise communities to seek and receive essential maternal and child health services by supporting the government in their training and mentoring.
We develop job aids and tools to support the Frontline Workers to easily communicate and educate the women in the community
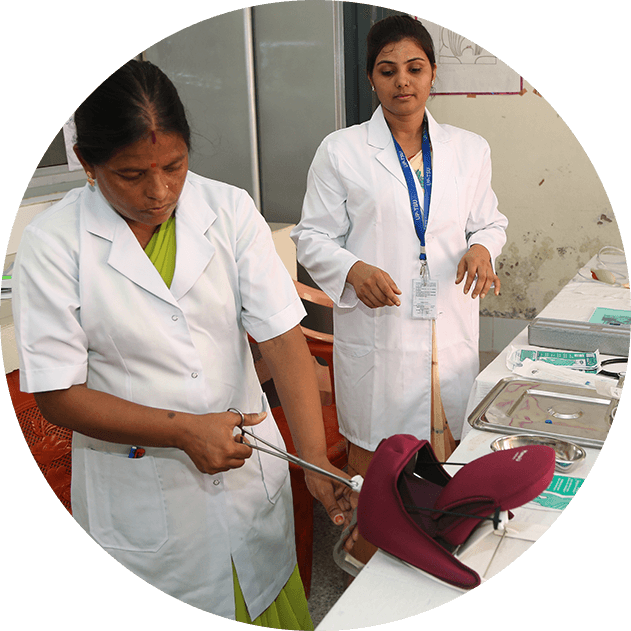


IHAT works towards improving the quality of Emergency Obstetric & Newborn care (Comprehensive and Basic) and paediatric services by strengthening knowledge, skills and practice of service providers.
The Nurse Mentors model provides on-site mentoring to the staff nurses to build their capacity on critical maternal and child health practices while the Regional Resource Training Center Training ropes in faculty from the medical colleges to mentor specialist doctors at first referral units to activate/strengthen Comprehensive Emergency Obstetric & Newborn services.
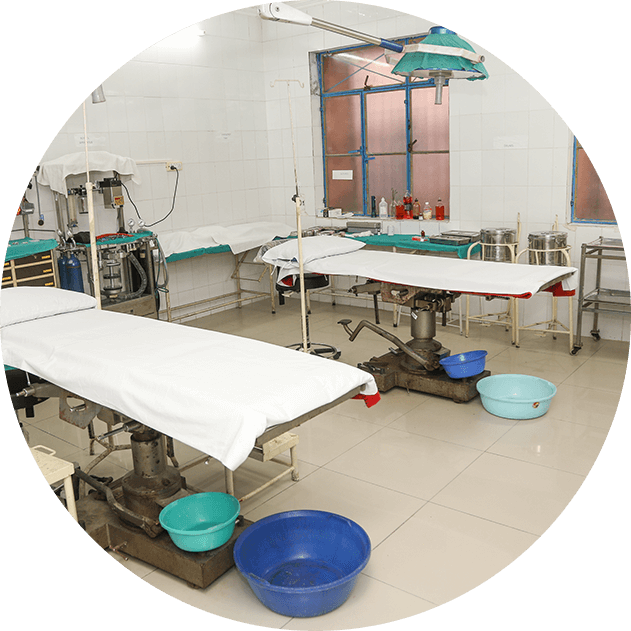
IHAT supports the government in conducting situational analysis to assess the availability of equipment, supplies and trained human resources for Emergency Obstetric & Newborn care (Comprehensive and Basic) and paediatric services.
It works with the government to develop micro-plans to address these gaps and facilitates the process where necessary.


The Uttar Pradesh Health Department, Government of Uttar Pradesh, launched Navjat Shishu Suraksha Karyakram (NSSK) to reduce neonatal mortality from birth asphyxia by training Staff Nurses and ANMs. The evaluation revealed gaps like inconsistent knowledge transfer and limited practical exposure. The program was revised to integrate adult learning principles, hands-on training, and better facilitator-to-participant ratios, ensuring uniform skill acquisition and improved newborn care.
Read More
Launched in 2008, the Government of Uttar Pradesh’s SBA training aimed to enhance maternal and neonatal care by training nurses and ANMs in delivery management. However, challenges like slow rollout and inconsistent quality persisted, which led to the conceptualisation of the Cluster Model, which improved training speed and quality through decentralised sites, local trainers, and mini-skill labs.
Read More
Government of Uttar Pradesh launched the Uttar Pradesh ke Swasthya Kendra (UPkSK) platform in July 2021 to address healthcare challenges exposed by Covid-19 pandemic. Built on the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM) framework, it centralises health facility data, improving resource allocation and service delivery. UPkSK integrates multiple systems, including HR, drug management, and service delivery, serving as a comprehensive digital tool for healthcare management in Uttar Pradesh.
Read More1 Sample Registration System – Special Bulletin on Maternal Mortality in India 2007-09
2 Sample Registration System – Special Bulletin on Maternal Mortality in India 2018-20
3 WHO Report on Maternal Mortality
4 One is too many: Ending child deaths from pneumonia and diarrhoea
5 Sample Registration System Statistical Report 2011
6 Sample Registration System Statistical Report 2020
7 WHO – Child mortality (under 5 years)